Working Time
Working Time
Book Appointment
Book Appointment
+
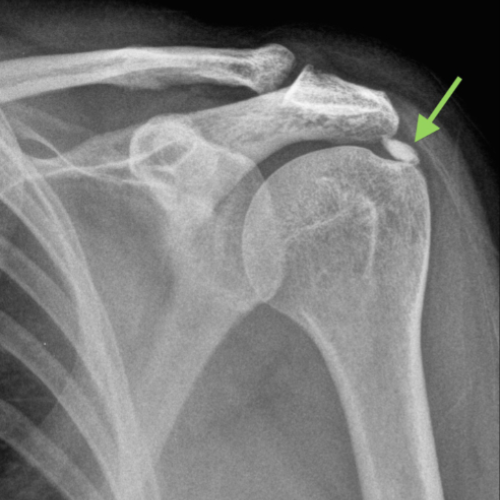
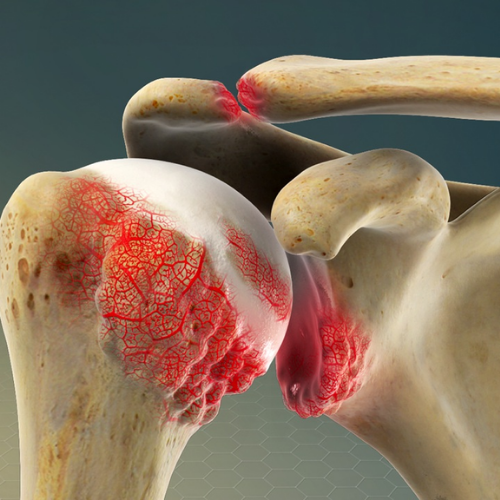
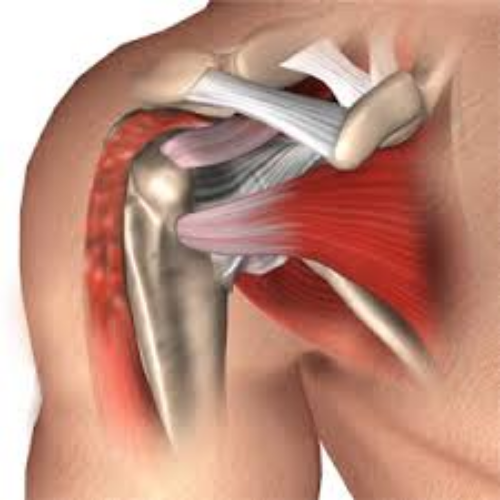
Glenoid labral tears are a prevalent cause of shoulder pain, often coexisting with conditions like rotator cuff tears, impingement, and glenohumeral arthritis. The complexity of these tears requires careful evaluation, and regenerative techniques like Comprehensive Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) with Prolotherapy have shown promising results, particularly in cases not suitable for arthroscopic repair.
Causes of Glenoid Labral Tears:
Symptoms of Glenoid Labral Tears:
Treatment Options for Glenoid Labral Tears:
Conservative Management
Surgical Intervention
Rehabilitation
Consultation with Dr. Tushar:
If you're experiencing symptoms suggestive of a glenoid labral tear or have been diagnosed with this condition, consult with Dr. Tushar for expert evaluation and personalised treatment recommendations.
Our specialist in pain management and musculoskeletal disorders, Dr. Tushar can help you navigate the various treatment options available and develop a comprehensive plan to address your shoulder pain and restore function. Schedule a consultation today to take the first step toward recovery.