Working Time
Sunday - On Emergency
Working Time
Monday - Saturday : 09.00pm to 05.30pmSunday - On Emergency
Book Appointment
Book Appointment
+
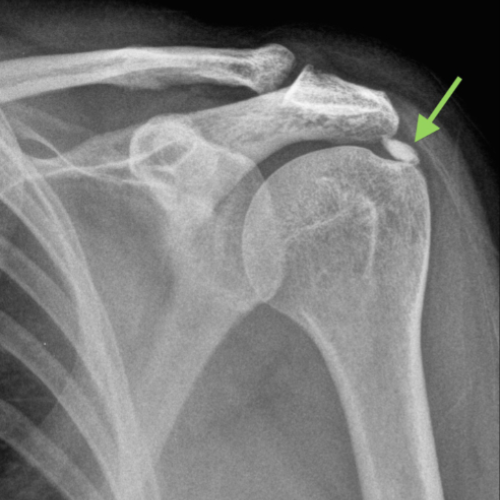
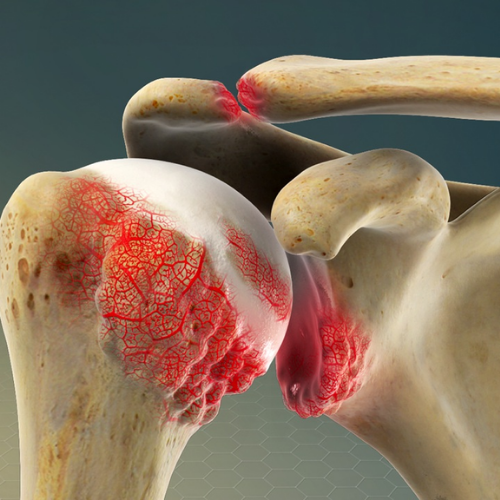
Shoulder calcific tendonitis, also known as calcific tendinitis or calcifying tendinitis, is a condition characterised by the formation of calcium deposits within the tendons of the shoulder, particularly the rotator cuff tendons. These deposits can cause inflammation, pain, and reduced range of motion in the shoulder joint.
Conditions:
Shoulder calcific tendonitis can occur in various tendons of the shoulder, including:
Symptoms:
Diagnosis:
Management:
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalised management of shoulder calcific tendonitis, including consideration of conservative treatments and interventional options such as injections or ultrasound-guided barbotage.