Working Time
Book Appointment
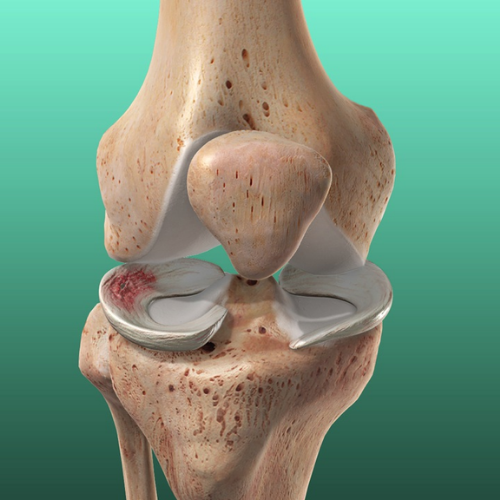
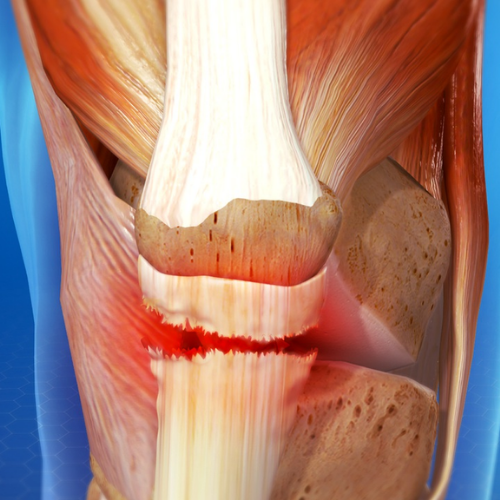
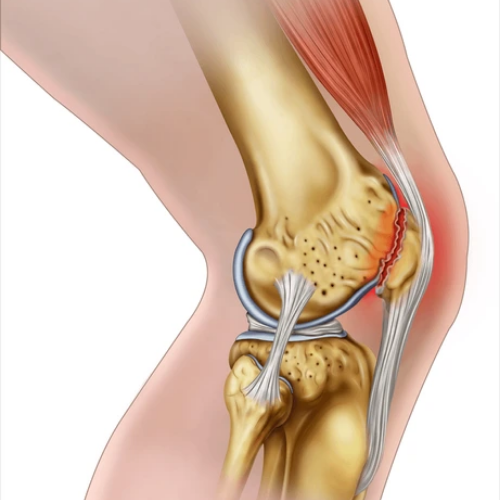
The knee meniscus is a crucial component of the knee joint, providing stability, load distribution, and cushioning. Injuries to the meniscus are common, often resulting from twisting or direct impact on the knee. Recognizing the symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and exploring treatment options for knee meniscus injuries are crucial for effective management.
Causes of Knee Meniscus Injuries:
Twisting Movements: Sudden twists or pivots during sports or activities.
Direct Impact: Forceful impact to the knee, common in contact sports.
Degeneration: Gradual wear and tear over time, more common with ageing.
Symptoms of Meniscus Tears:
Pain: Often on the side or centre of the knee, worsening with movement.
Swelling: Rapid onset of swelling, indicating inflammation.
Stiffness: Difficulty in fully extending or flexing the knee.
Popping or Clicking: Audible sounds during movement.
Locking: Inability to fully straighten the knee due to a torn fragment.
Instability: Feeling of the knee giving way or buckling.
Treatment Options:
Initial Evaluation:
A thorough evaluation by a Pain specialist is essential to assess the extent and severity of the meniscus injury, determine associated injuries, and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Conservative Management:
Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE), Physical Therapy,
Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the knee joint
can provide short-term relief of pain and inflammation associated with meniscus injuries.
Viscosupplementation:Hyaluronic Acid injections (viscosupplements) can be injected into the knee joint to improve lubrication and reduce friction, providing relief of symptoms such as pain and stiffness.
Regenerative Therapy:
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections, which contain concentrated platelets and growth factors obtained from the patient's own blood, may promote tissue healing and regeneration in the injured meniscus.
Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate (BMAC) Therapy: BMAC involves aspirating bone marrow from the patient's hip bone and concentrating the stem cells and growth factors present in the bone marrow. The concentrated solution is then injected into the injured meniscus to promote tissue healing and regeneration.
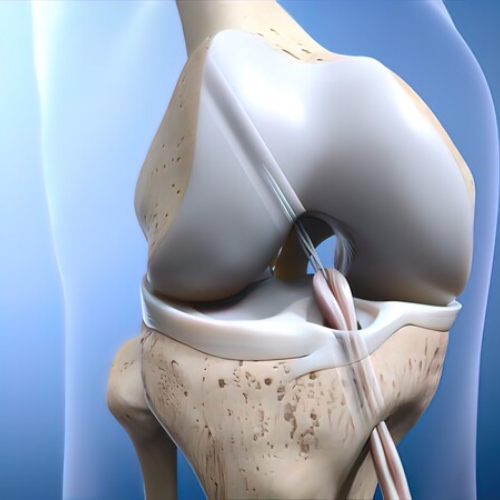
Ultrasound (US) guidance can be used to visualise the target area within the knee joint and guide the needle placement for accurate delivery of regenerative therapies such as PRP and BMAC.
Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe meniscus injuries that do not respond to conservative treatments or regenerative therapy, surgical intervention such as meniscal repair, meniscectomy (partial removal of the meniscus), or meniscal transplantation may be necessary to alleviate symptoms and restore knee function.
For personalised knee care and expert guidance, consult with Dr. Tushar, specialising in knee health and rehabilitation.