Working Time
Book Appointment
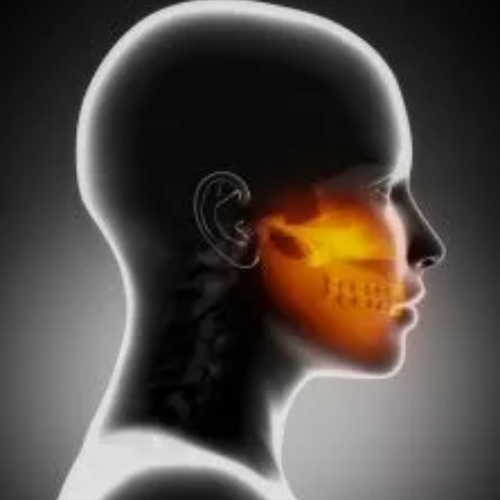
Trigeminal neuralgia is a chronic pain condition characterised by sudden, severe, and recurrent episodes of facial pain. This pain is typically sharp, stabbing, or electric shock-like and is often triggered by trivial stimuli such as touching the face, chewing, or speaking. Trigeminal neuralgia affects the trigeminal nerve, which is responsible for transmitting sensations from the face to the brain. The condition can significantly impact a person's quality of life, causing difficulty with eating, speaking, and performing daily activities.
Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia:
Compression of the trigeminal nerve: Pressure on the trigeminal nerve by a blood vessel or tumour can lead to trigeminal neuralgia.
Multiple sclerosis (MS): In some cases, damage to the myelin sheath surrounding the trigeminal nerve due to MS can cause trigeminal neuralgia.
Ageing: Trigeminal neuralgia is more common in older adults, and age-related changes may contribute to the condition.
Facial trauma: Injuries to the face or head can damage the trigeminal nerve, leading to trigeminal neuralgia.
Idiopathic: In some cases, the cause of trigeminal neuralgia is unknown, and it is referred to as idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia.
Treatments for Trigeminal Neuralgia:
Medications:
Anticonvulsant drugs: Medications such as carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, or gabapentin can help reduce nerve pain in trigeminal neuralgia.
Muscle relaxants: Drugs like baclofen may be prescribed to relieve muscle spasms that can trigger facial pain.
Nerve Blocks: Local anaesthetic injections or nerve blocks targeting the trigeminal nerve can provide short-term relief from trigeminal neuralgia pain.
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
RFA is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat trigeminal neuralgia by targeting the specific branch of the trigeminal nerve involved in the condition. During RFA, a specialised needle is inserted near the affected nerve branch, and radiofrequency energy is applied to create a lesion that disrupts the nerve's ability to transmit pain signals. This procedure offers targeted pain relief for patients with trigeminal neuralgia, providing long-lasting relief from the debilitating facial pain associated with the condition. The specific branch of the trigeminal nerve targeted for RFA depends on the location and distribution of the patient's pain, and the procedure is typically performed under fluoroscopic guidance to ensure precise needle placement and optimal outcomes.
Seeking evaluation and guidance from Dr. Tushar, a healthcare professional experienced in managing chronic pain conditions, is essential for individuals suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. Dr. Tushar can assess your specific symptoms, medical history, and treatment goals to develop a personalised treatment plan.