Working Time
Working Time
Book Appointment
Book Appointment
+
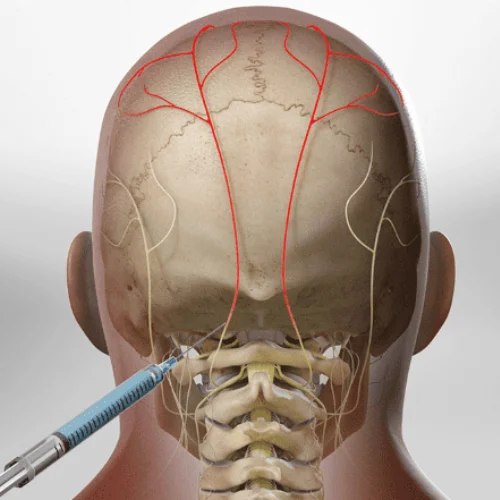
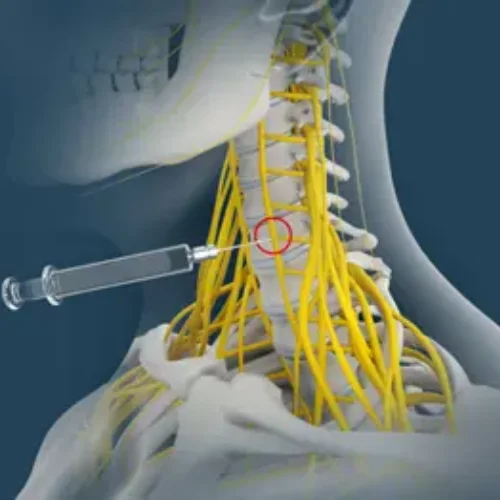
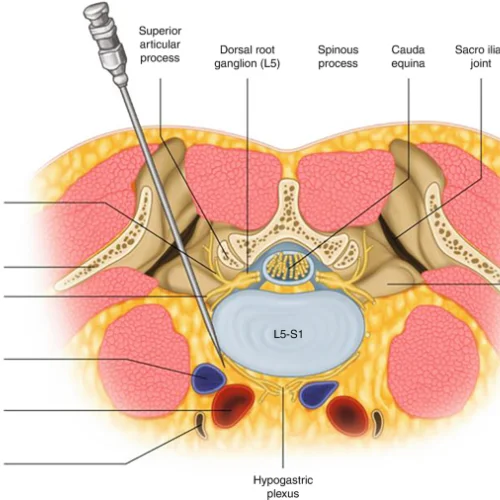
An occipital nerve block is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the injection of a local anaesthetic and, in some cases, a corticosteroid near the occipital nerves, which are located at the base of the skull. This procedure aims to relieve Dr. Tushar's clinic pain in the head, neck, and upper shoulder regions, often associated with conditions like tension headaches or occipital neuralgia.
- Indications:
- Occipital Neuralgia:
- This condition involves irritation or inflammation of the occipital nerves, causing sharp, shooting pain in the back of the head or upper neck.
- Occipital nerve blocks can provide both diagnostic information and therapeutic pain relief for individuals with occipital neuralgia.
- Tension Headaches:
- Tension headaches, characterized by a constant, dull pain or pressure around the head, can benefit from occipital nerve blocks.
- The procedure may help reduce the frequency and severity of tension headaches.
- Procedure:
- Patient Positioning: The patient is usually positioned seated or lying down. Vital signs may be monitored.
- Preparation: The skin over the injection site is cleaned, and a local anesthetic is applied to numb the area, minimizing discomfort during the procedure.
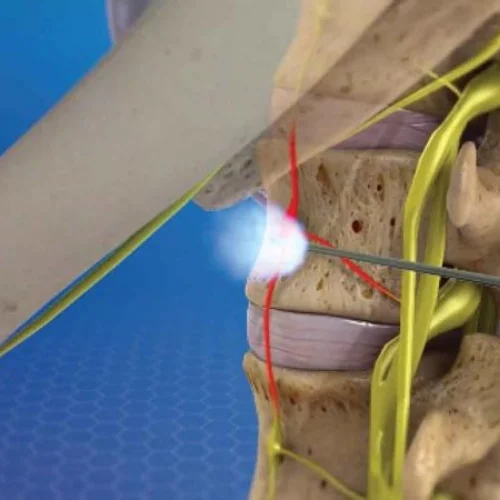
- Needle Placement:
- Using fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance, a thin needle is carefully inserted near the occipital nerves.
- Placement accuracy is confirmed through real-time imaging.
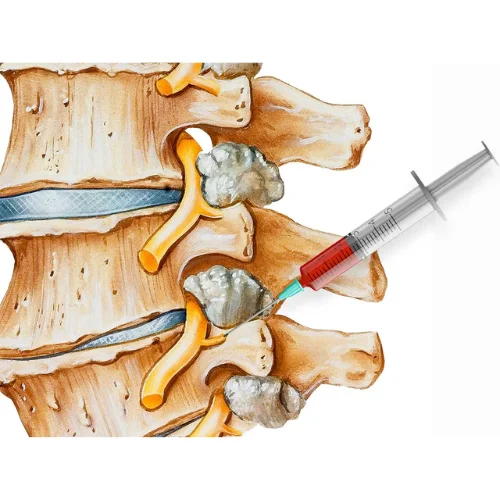
- Injection of Medication:
- A mixture of local anesthetic and, if indicated, a corticosteroid is injected around the occipital nerves.
- The medication aims to reduce inflammation and block pain signals.
- Post-Procedure Observation: The patient is monitored for a short period after the injection to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions.
- Expected Outcomes:
- Pain Relief:
- Occipital nerve blocks can provide immediate pain relief due to the local anesthetic.
- For some individuals, the corticosteroid component may offer more extended pain relief by reducing inflammation.
- Diagnostic Value: If the occipital nerve block provides significant pain relief, it can serve as a diagnostic tool, confirming the occipital nerves' contribution to the pain.
- Post-Procedure Considerations:
- Temporary Discomfort: Mild soreness at the injection site is common and usually resolves within a day or two. Patients can resume normal activities after a brief recovery period.
- Follow-Up:
- Occipital nerve blocks may need to be repeated for sustained pain relief.
- Follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are essential to assess the procedure's effectiveness and discuss further management options.
- Potential Risks: Occipital nerve blocks are generally safe, but as with any medical procedure, there are minimal risks, including infection or bleeding at the injection site.