Working Time
Book Appointment
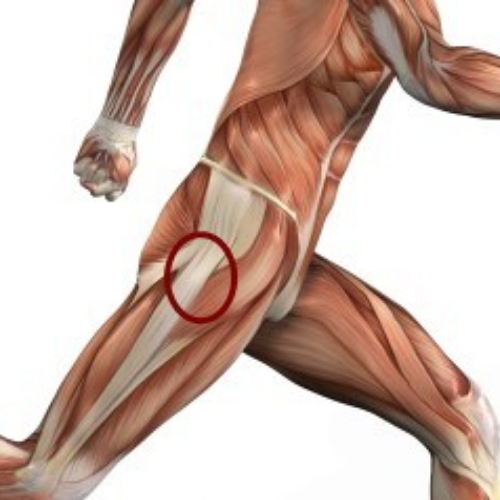
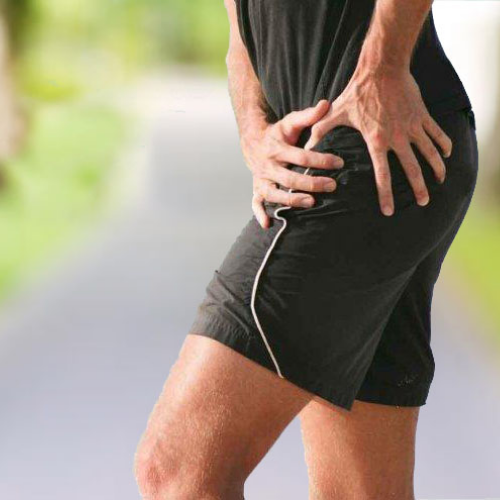
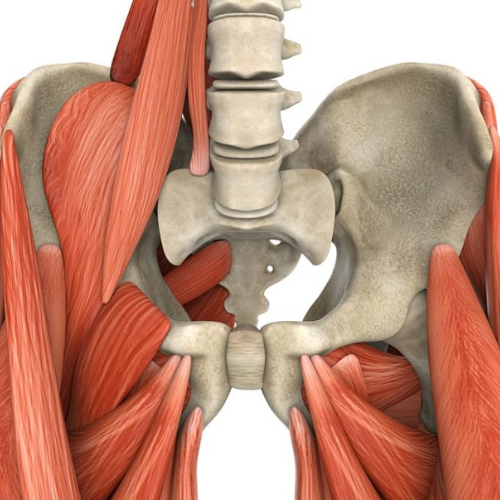
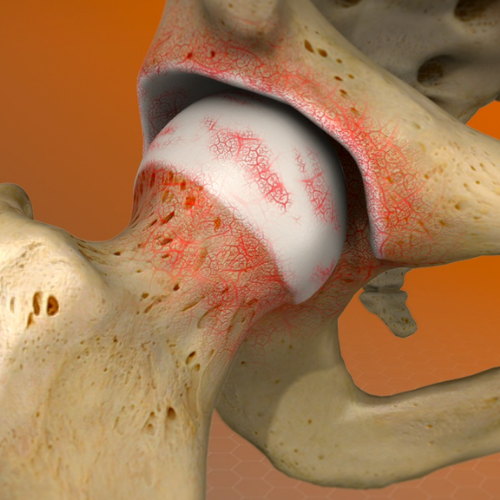
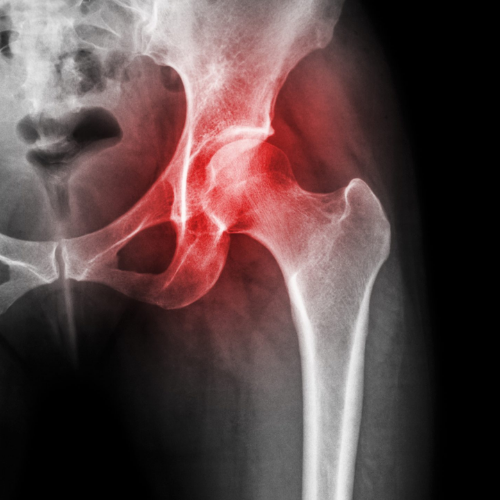
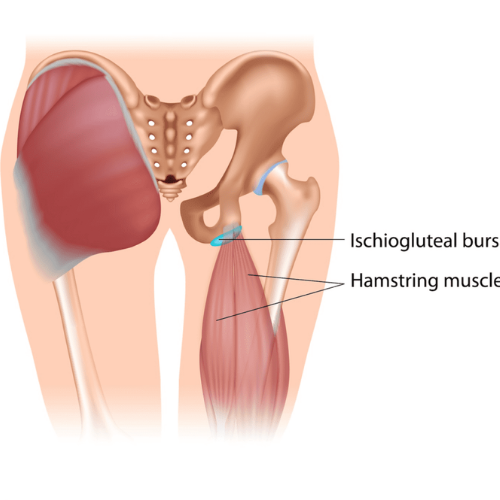
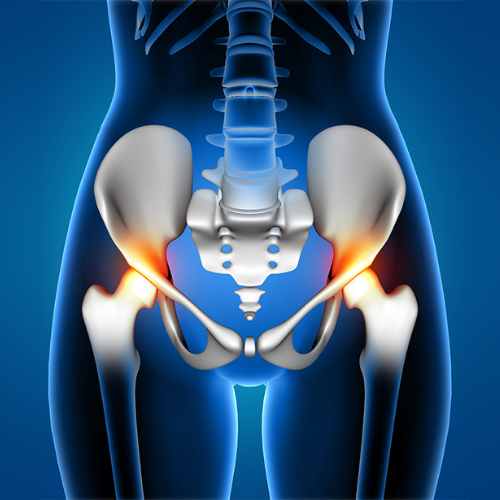
Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS), also known as lateral hip pain, is a condition characterised by pain and tenderness over the greater trochanter, the bony prominence on the side of the hip. It is often caused by inflammation or injury to the tissues surrounding the greater trochanter.
Causes:
Overuse or Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repetitive hip motion or prolonged standing, such as running or climbing stairs, can lead to irritation of the tissues around the greater trochanter.
Muscle Weakness or Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance in the muscles around the hip, particularly the gluteus Medius, can contribute to GTPS.
Trauma: Direct trauma to the hip, such as a fall or blow to the hip, can cause inflammation and pain.
Poor Biomechanics: Abnormalities in hip or lower limb biomechanics, such as leg length discrepancy or foot pronation, can increase the risk of GTPS.
Previous Hip Surgery: Individuals who have undergone hip surgery, such as hip replacement or repair, may be at increased risk of developing GTPS.
Treatments:
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate the pain and modifying activities to reduce stress on the hip can help Dr. Tushar's clinic symptoms.
Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises for the hip muscles, as well as stretching exercises to improve flexibility, can help improve hip biomechanics and reduce pain.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and pain.
Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections into the greater trochanteric bursa can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.
Regenerative therapy
PRP injections are thought to stimulate tissue repair and regeneration, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of the damaged tendons. This can lead to pain relief and improved function. PRP therapy is often used as a non-surgical treatment option for tendon injury, particularly in cases where conservative measures such as rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications have not provided sufficient relief.
Surgery: In severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical options such as bursectomy (removal of the inflamed bursa) or gluteal tendon repair may be considered.
If you are experiencing persistent lateral hip pain or other symptoms of GTPS, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Dr. Tushar can provide expert guidance and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.